A toothache is more than just an inconvenience — it can be a sign of a serious dental infection that should never be ignored. If left untreated, an infected tooth can lead to pain, tooth loss, and in extreme cases, life-threatening complications. But how do you know if your toothache is just sensitivity or something more serious?
In this article, we’ll explore the common signs of an infected tooth, how to recognize danger early, and what you should do to protect your oral and overall health.
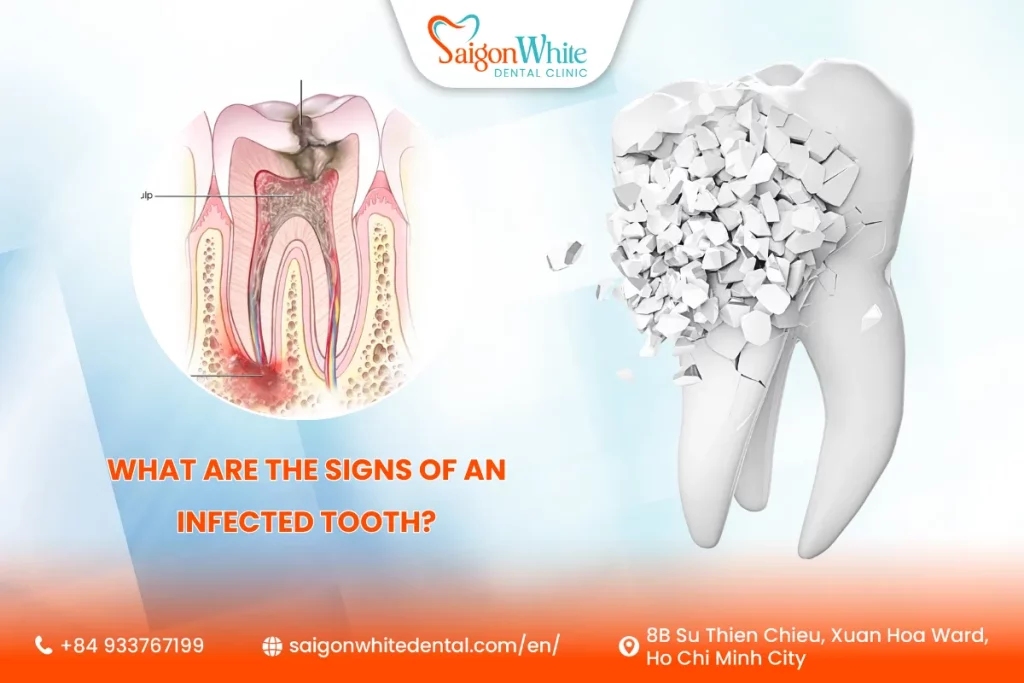
What Is a Tooth Infection?
A tooth infection occurs when bacteria enter the inner layers of the tooth or surrounding tissues. The infection can start small — from a cavity or cracked enamel — and slowly spread deeper until it reaches the pulp, bone, or even bloodstream.
There are three main types of tooth infections:
1. Pulpal Infection
When bacteria reach the tooth’s inner pulp (where nerves and blood vessels reside), it causes inflammation and pain. This is often the result of untreated decay or tooth trauma.
2. Periapical Abscess
An abscess is a pocket of pus that forms at the tip of the tooth root due to severe bacterial infection. It may cause swelling and pain that radiates to other areas.
3. Periodontal Infection
This occurs in the gums and supporting tissues around the teeth, usually as a result of advanced gum disease (periodontitis). It can spread to nearby teeth and bone if not treated.
Common Causes Include:
- Deep cavities
- Cracked or chipped teeth
- Failed dental work (like old fillings or crowns)
- Poor oral hygiene
- Gum disease
- Traumatic injuries to the mouth
Common Signs and Symptoms of an Infected Tooth
Recognizing the signs of a tooth infection early can save your tooth and prevent serious complications. Let’s explore the most telling symptoms:
Persistent or Severe Toothache

This is the most obvious symptom. The pain can be:
- Throbbing, sharp, or shooting
- Constant or intermittent
- Worse when chewing, biting, or lying down
Pain that doesn’t go away with over-the-counter painkillers or lasts more than a couple of days is a red flag.
Sensitivity to Hot or Cold

If you feel sharp pain or discomfort when drinking hot coffee or eating ice cream, and the sensation lingers, it could indicate an issue deeper inside the tooth — such as nerve exposure or infection.
Temporary sensitivity is common, but ongoing or worsening sensitivity often suggests infection.
Swollen or Red Gums
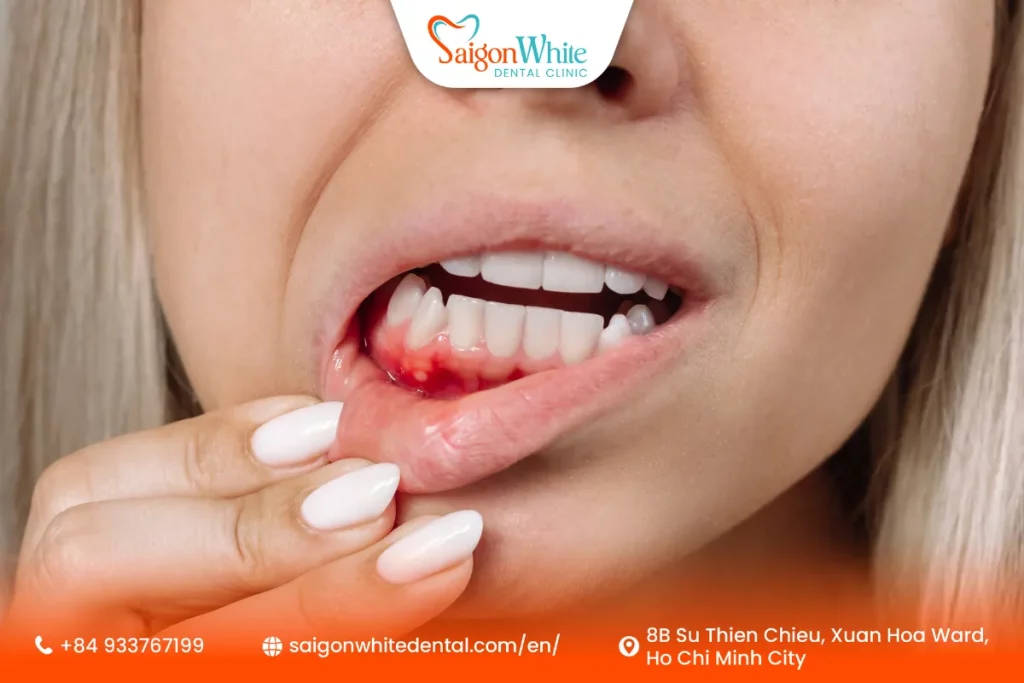
Infected teeth often cause inflammation in the gums surrounding them. This can appear as:
- A red, swollen area near the infected tooth
- Puffy or tender gum tissue
- Painful to touch or brush
Sometimes, a pimple-like bump appears on the gum — known as a dental abscess — which may ooze pus.
Bad Breath or Foul Taste in the Mouth

As bacteria and decaying tissue accumulate, they can produce a strong odor or an unpleasant taste. If you suddenly experience halitosis or a metallic taste that brushing doesn’t eliminate, this may be a sign of infection or pus leakage.
Pus or Drainage
Visible pus around the tooth or gums is a clear indication that your body is fighting off infection. You may notice it draining from a gum bump or taste it in your mouth.
This typically means an abscess has formed and needs professional attention right away.
Facial or Jaw Swelling
If an infection spreads beyond the tooth and gum, it can cause:
- Swelling in the cheek or jaw
- Puffy appearance around the mouth or eye
- Tightness or restricted movement of the jaw
Swelling that worsens quickly or affects your ability to open your mouth is considered a dental emergency.
Fever or General Fatigue
Your body may develop a low-grade or high fever to fight the infection. Combined with fatigue or chills, this suggests the infection is spreading. Some people also experience headaches or neck pain.
If you feel sick and suspect it’s coming from a tooth, seek immediate care.
Swollen Lymph Nodes
Lymph nodes under the jaw or in the neck may swell and become tender when infection spreads beyond the local tooth area.
These are part of the body’s immune system and often swell when fighting serious infections.
Emergency Signs You Should Never Ignore
Certain symptoms indicate that a tooth infection has progressed to a dangerous level and may be spreading to other parts of your body.
Seek immediate medical care if you experience:
- High fever (above 101°F or 38.5°C)
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing
- Severe swelling in the face, neck, or eye area
- Rapid heartbeat or confusion
- A firm or shiny swelling under the jaw or near the throat
These may be signs of sepsis, a life-threatening reaction to infection.
How Dentists Diagnose a Tooth Infection
If you suspect your tooth is infected, a dentist can confirm it with:
Clinical Examination
- Checking for swelling, redness, pus, or gum abnormalities
- Testing for tooth mobility or pain when touched
Dental X-rays
- Reveal if there is bone loss, an abscess, or signs of decay under the surface.
- Help determine if the infection has spread to other teeth or tissues
Sensitivity and Tapping Tests
- Cold or heat tests to check nerve response
- Gentle tapping to assess pain and inflammation
Accurate diagnosis is key to recommending the correct treatment and preventing further complications.
What Happens If You Leave a Tooth Infection Untreated?
Leaving a tooth infection untreated can have serious consequences — not just for your oral health, but for your entire body. While the pain may come and go, the underlying infection does not resolve on its own and can lead to more dangerous complications over time.
Here’s What Can Happen If You Don’t Treat a Tooth Infection:
Worsening Pain and Swelling
- The infection can spread deeper into the tooth, gums, and jawbone, leading to intense throbbing pain, pressure, and facial swelling.
- What started as a small cavity or mild discomfort can escalate quickly.
Tooth Loss
- As the infection spreads, it damages the bone supporting your tooth.
- If left untreated, the tooth may loosen and fall out or need to be extracted.
Spread to Surrounding Tissues (Abscess Formation)
- Untreated infections can lead to a dental abscess — a pocket of pus that causes pain, swelling, and possibly a visible bump on the gums.
- Abscesses can rupture and spread bacteria to other areas of the face and neck.
Jawbone Deterioration
- Chronic infections can lead to bone loss in the jaw, making future dental work (like implants or bridges) more difficult or impossible without bone grafting.
Sinus Infections
- Infections in the upper teeth can spread into the sinus cavities, causing sinusitis, pressure headaches, and nasal issues.
Systemic Infection (Sepsis)
- If the bacteria enter your bloodstream, it can lead to sepsis, a life-threatening condition that affects the entire body.
- Symptoms include high fever, chills, rapid heartbeat, confusion, and even organ failure.
Infection Spread to Brain or Heart (Rare but Severe)
- In rare cases, untreated dental infections can spread to the brain (brain abscess) or heart (endocarditis) — both medical emergencies.
Treatment Options for an Infected Tooth
Treatment will depend on the severity of the infection and how far it has spread.
Antibiotics
Prescribed to fight infection and reduce inflammation. Antibiotics do not cure the infection alone — they control it while further dental treatment is prepared.
Root Canal Treatment
If the pulp is infected but the tooth is still salvageable, your dentist may perform a root canal to remove the infected tissue, clean the canal, and seal it to prevent reinfection.
Tooth Extraction
If the tooth is too damaged or the infection has destroyed the surrounding bone, removal may be the only option. This is followed by options like dental implants or bridges.
Abscess Drainage
If pus buildup is present, the dentist may make an incision to drain the abscess and relieve pressure.
Can a Tooth Infection Go Away on Its Own?
No. A dental infection will not resolve without proper intervention. In some cases, pain may go away as the nerve dies, but the infection remains — often growing and spreading quietly.
Self-medicating with painkillers or home remedies may ease discomfort, but it won’t eliminate the source of the infection. Only a dentist can fully clean and treat the area.
How to Prevent a Tooth Infection
The good news is: most tooth infections are entirely preventable with good oral hygiene and regular check-ups.
Prevention tips:
- Brush twice daily with fluoride toothpaste
- Floss once a day to remove food and plaque
- Avoid sugary snacks and drinks that promote decay
- Visit the dentist every 6 months for cleaning and exams
- Treat cavities, chips, or broken teeth promptly
- Wear a mouthguard if you grind your teeth at night
Prevention is not just about avoiding pain — it’s about protecting your smile and overall health for the long run.
Conclusion
Tooth infections are not just about discomfort — they can be serious and even dangerous if ignored. By recognizing early signs of an infected tooth — such as persistent pain, swelling, pus, or fever — you can act quickly and avoid long-term complications.
If you suspect your tooth may be infected, don’t wait. Early treatment could save your tooth, protect your health, and save you from costly procedures later.
Need Help With a Painful or Infected Tooth?
At Saigon White Dental, our experienced dentists provide fast, gentle, and effective care for infected teeth and abscesses. We offer advanced diagnostics, root canal therapy, and emergency dental services for both locals and international patients.
=> Visit our modern clinic in Ho Chi Minh City
=> Book your appointment today

 Book now
Book now